All Publications
A list of All Publications (Chronological Order) can be found here.
Selected Publications
1. Decentralized and Distributed Learning at Scale
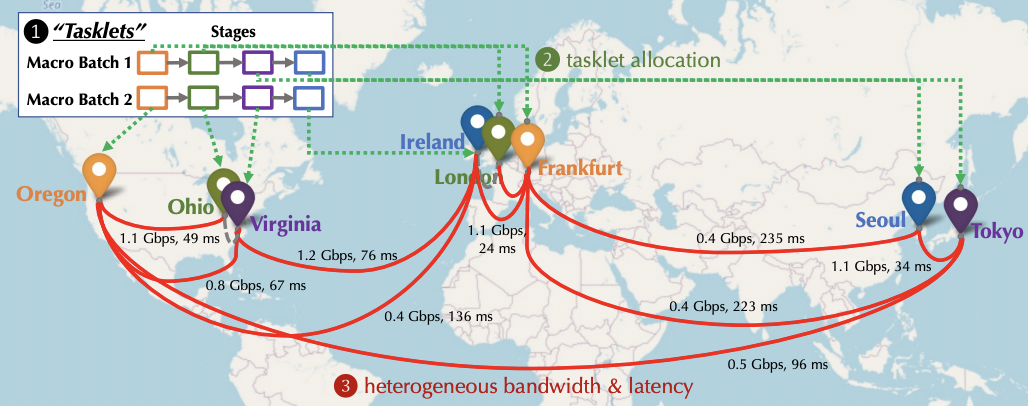 Binhang Yuan, Yongjun He, Jared Quincy Davis, Tianyi Zhang, Tri Dao, Beidi Chen, Percy Liang, Christopher Re, Ce Zhang. Decentralized Training of Foundation Models in Heterogeneous Environments. NeurIPS 2022 (Oral Presentation 186/9600 = 1.9% submissions)
Binhang Yuan, Yongjun He, Jared Quincy Davis, Tianyi Zhang, Tri Dao, Beidi Chen, Percy Liang, Christopher Re, Ce Zhang. Decentralized Training of Foundation Models in Heterogeneous Environments. NeurIPS 2022 (Oral Presentation 186/9600 = 1.9% submissions)
Training large langauge models over decentralized geo-distributed devices
(500Mbps bandwidth, 100ms latency). It is possible if we carefully schedule
the network considering hetergenous network conditions!
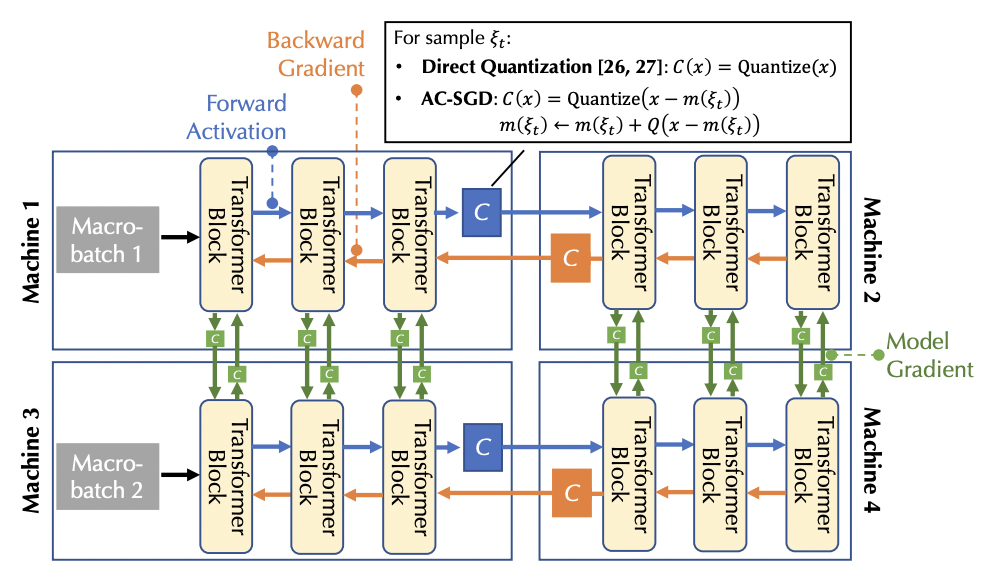 Jue WANG, Binhang Yuan, Luka Rimanic, Yongjun He, Tri Dao, Beidi Chen, Christopher Re, Ce Zhang. Fine-tuning Language Models over Slow Networks using Activation Quantization with Guarantees. NeurIPS 2022.
Jue WANG, Binhang Yuan, Luka Rimanic, Yongjun He, Tri Dao, Beidi Chen, Christopher Re, Ce Zhang. Fine-tuning Language Models over Slow Networks using Activation Quantization with Guarantees. NeurIPS 2022.
Compressing forward activations in pipeline parallelism requires careful
thinking --- If not careful, it introduces bias in the gradient and hurts
the convergence. This paper provides, to our best knowledge, one of the
first compression scheme that leads to an unbiased convergence, and enables
decentralized training of large language models over slow networks
(e.g., <300Mbps). The secret is to compress the difference! Enabling
decentralized training
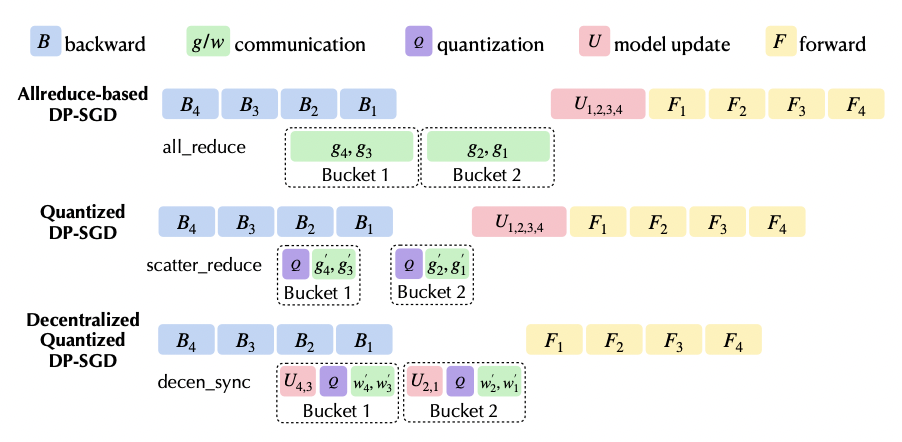 Shaoduo Gan, Xiangru Lian, Rui Wang, Jianbin Chang, Chengjun Liu, Hongmei Shi, Shengzhuo Zhang, Xianghong Li, Tengxu Sun, Jiawei Jiang, Binhang Yuan, Sen Yang, Ji Liu, Ce Zhang. BAGUA: Scaling up Distributed Learning with System Relaxations. VLDB 2022.
Shaoduo Gan, Xiangru Lian, Rui Wang, Jianbin Chang, Chengjun Liu, Hongmei Shi, Shengzhuo Zhang, Xianghong Li, Tengxu Sun, Jiawei Jiang, Binhang Yuan, Sen Yang, Ji Liu, Ce Zhang. BAGUA: Scaling up Distributed Learning with System Relaxations. VLDB 2022.
A unified distributed learning framework that supports a diverse range of
communication-efficient algorithms taking advantage of (1) asynchrony,
(2) decentralization, (3) communication compression, and (4) their combinations.
The key is a declarative optimization framework that manages communication and
computation. Change one line of code to use BaguaStrategy in Pytorch Lightning
and speedup your training over Horovod and BytePS even in data center networks
and expect much larger speedups in slow networks!
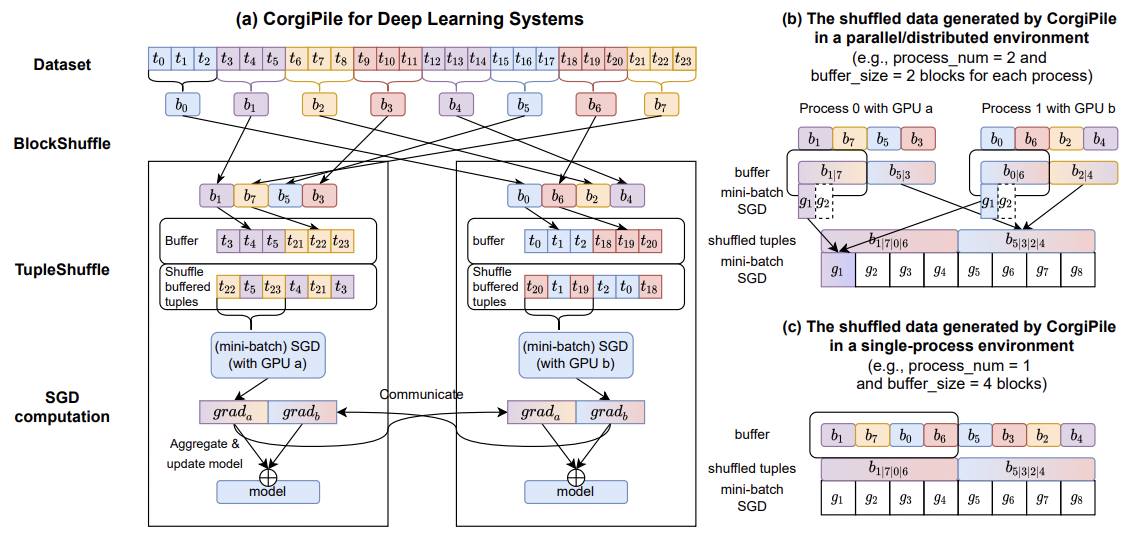 Lijie Xu, Shuang Qiu, Binhang Yuan, Jiawei Jiang, Cedric Renggli, Shaoduo Gan, Kaan Kara, Guoliang Li, Ji Liu, Wentao Wu, Jieping Ye, Ce Zhang. In-Database Machine Learning with CorgiPile: Stochastic Gradient Descent without Full Data Shuffle. SIGMOD 2022.
Lijie Xu, Shuang Qiu, Binhang Yuan, Jiawei Jiang, Cedric Renggli, Shaoduo Gan, Kaan Kara, Guoliang Li, Ji Liu, Wentao Wu, Jieping Ye, Ce Zhang. In-Database Machine Learning with CorgiPile: Stochastic Gradient Descent without Full Data Shuffle. SIGMOD 2022.
Optimizing training over large datasets stored on disks, which can be used for
both Tensorflow FileScanner and in-Database ML. On the ML side, a novel first-order
method that does not requires full data shuffle (with convergence guarantees)
and thus I/O efficient. On the system, a novel in-database ML framework that
integrates ML physically into DB. Check out this algorithm in OpenGauss and
expect up to two orders of magnitude speedups over MADlib. Also available
as a new Tensorflow FileScanner.
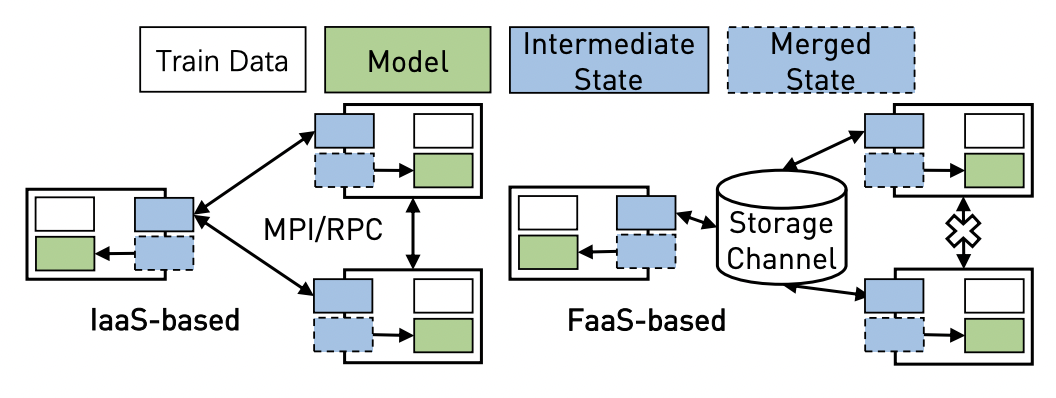 Jiawei Jiang, Shaoduo Gan, Yue Liu, Fanlin Wang, Gustavo Alonso, Ana Klimovic, Ankit Singla, Wentao Wu, Ce Zhang. Towards Demystifying Serverless Machine Learning Training. SIGMOD 2021.
Jiawei Jiang, Shaoduo Gan, Yue Liu, Fanlin Wang, Gustavo Alonso, Ana Klimovic, Ankit Singla, Wentao Wu, Ce Zhang. Towards Demystifying Serverless Machine Learning Training. SIGMOD 2021.
Systematic depiction of the tradeoff space of training machine learning models
over serverless infrastructure. When does serverless make sense for ML training?
How should serverless infrastructure evolves to better support ML?
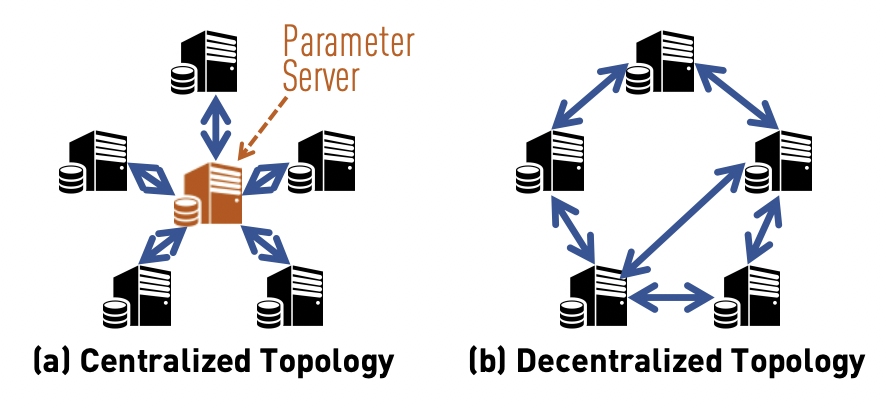 X Lian, Ce Zhang, H Zhang, CJ Hsieh, W Zhang, J Liu. Can Decentralized Algorithms Outperform Centralized Algorithms? A Case Study for Decentralized Parallel Stochastic Gradient Descent. NIPS 2017. (Oral Presentation)
X Lian, Ce Zhang, H Zhang, CJ Hsieh, W Zhang, J Liu. Can Decentralized Algorithms Outperform Centralized Algorithms? A Case Study for Decentralized Parallel Stochastic Gradient Descent. NIPS 2017. (Oral Presentation)
A Gossip-style algorithm for decentralized learning --- instead of all workers
exchange information with everyone, information is propagated by each machine
only talking to two neighbors. More surprisingly, this algorithm has the same
convergence rate (in O(-) sense) as its centralized counterpart. Decentralized
learning can be efficient, if we co-design the algorithm and the system together!
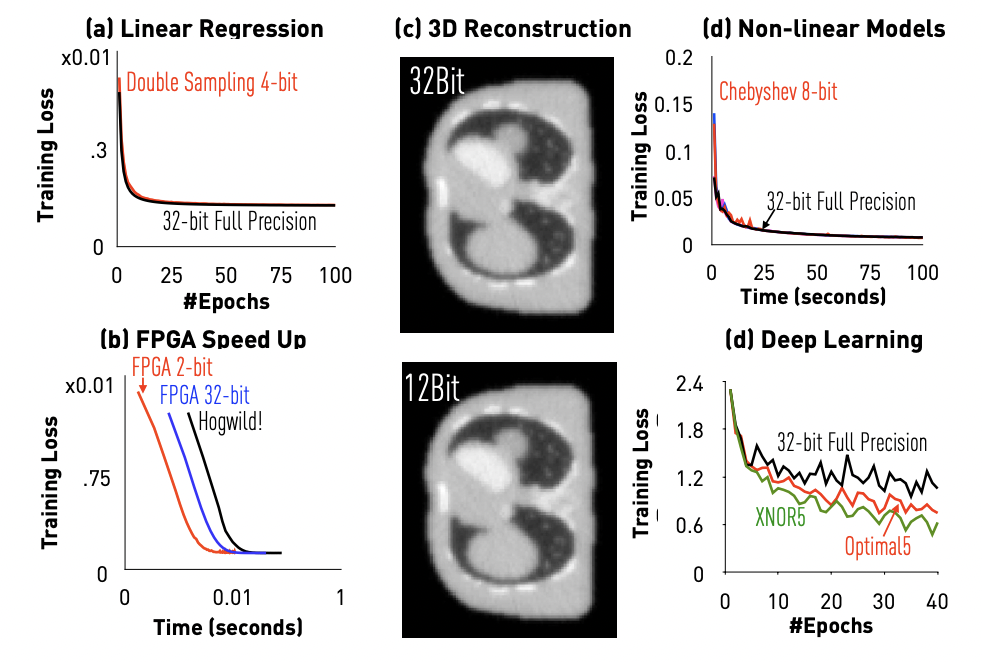 H Zhang, J Li, K Kara, D Alistarh, J Liu, Ce Zhang. The ZipML Framework for Training Models with End-to-End Low Precision: The Cans, the Cannots, and a Little Bit of Deep Learning. ICML 2017.
H Zhang, J Li, K Kara, D Alistarh, J Liu, Ce Zhang. The ZipML Framework for Training Models with End-to-End Low Precision: The Cans, the Cannots, and a Little Bit of Deep Learning. ICML 2017.
Can we conduct lossy compression on the data when training ML models? This
question is delicate even for simple models such as linear regression. Different
from gradient, an unbiased compressor will lead to bias when it is applied to
data. In this paper, we propose a data compression framework and study its
application to a various models, from linear regression, to deep neural networks.
2. Data-centric MLOps
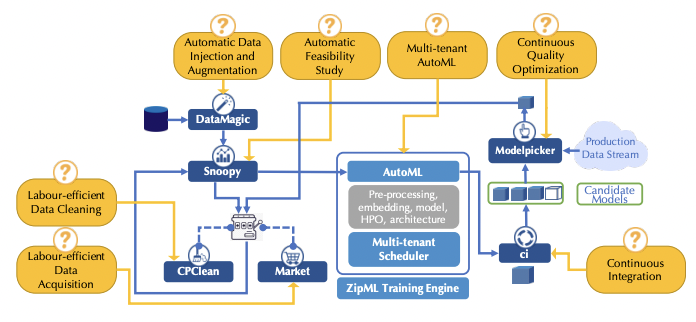 Leonel Aguilar, David Dao, Shaoduo Gan, Nezihe Merve Gurel, Nora Hollenstein, Jiawei Jiang, Bojan Karlas, Thomas Lemmin, Tian Li, Yang Li, Susie Rao, Johannes Rausch, Cedric Renggli, Luka Rimanic, Maurice Weber, Shuai Zhang, Zhikuan Zhao, Kevin Schawinski, Wentao Wu, Ce Zhang. Ease.ML: A Lifecycle Management System for Machine Learning. CIDR 2021.
Leonel Aguilar, David Dao, Shaoduo Gan, Nezihe Merve Gurel, Nora Hollenstein, Jiawei Jiang, Bojan Karlas, Thomas Lemmin, Tian Li, Yang Li, Susie Rao, Johannes Rausch, Cedric Renggli, Luka Rimanic, Maurice Weber, Shuai Zhang, Zhikuan Zhao, Kevin Schawinski, Wentao Wu, Ce Zhang. Ease.ML: A Lifecycle Management System for Machine Learning. CIDR 2021.
Building high-quality, trustworthy ML applications is not an easy task --- often
improving the quality of a model is a journey of improving the quality of the
underlying data. Users are desperately need help today to conduct these
"data iterations". Ease.ML is a framework that we developed over the years
that consists of a collection of tools to support this end-to-end process of
"data engineering for ML".
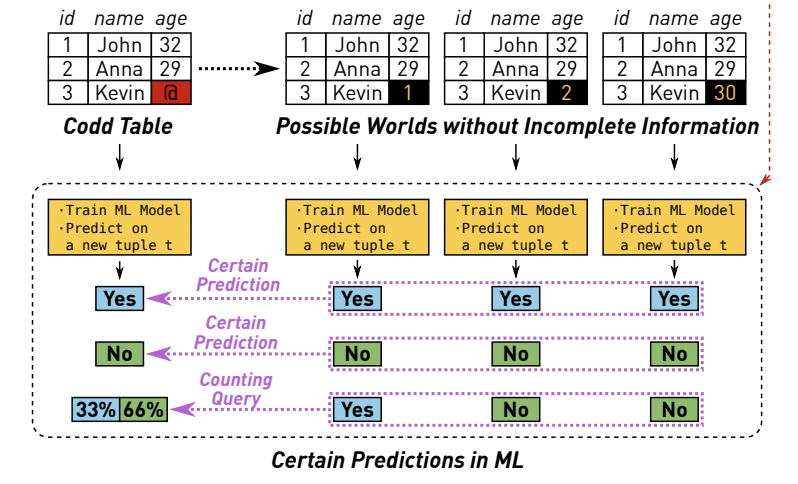 Bojan Karlas, Peng Li, Renzhi Wu, Nezihe Merve Gürel, Xu Chu, Wentao Wu, Ce Zhang. Nearest Neighbor Classifiers over Incomplete Information: From Certain Answers to Certain Predictions. VLDB 2021.
Bojan Karlas, Peng Li, Renzhi Wu, Nezihe Merve Gürel, Xu Chu, Wentao Wu, Ce Zhang. Nearest Neighbor Classifiers over Incomplete Information: From Certain Answers to Certain Predictions. VLDB 2021.
A principled framework for "Data Cleaning for ML" via information maximization.
Algorithmically, we show that computing Entropy, a key quantity for information
maximization, can be computed in PTIME for models with strong locality. This
is inspired by the notion of "Certain Answer" in database theory, and bring
together data and learning in a principled, yet computationally feasible way.
 Peng Li, Xi Rao, Jeffinifer Blase, Yue Zhang, Xu Chu, Ce Zhang. CleanML: A Benchmark for Evaluating the Impact of Data Cleaning on ML Classification Tasks. ICDE 2021.
Peng Li, Xi Rao, Jeffinifer Blase, Yue Zhang, Xu Chu, Ce Zhang. CleanML: A Benchmark for Evaluating the Impact of Data Cleaning on ML Classification Tasks. ICDE 2021.
Data quality has been studied intensively by the data management community for
decades, but how does noise and biases in the training data influence the
downstream ML model? This paper provides a systematic benchmark on this
fundamental question. In a quantitative way, we show that often data matters
much more than specific choices of models!
 Ruoxi Jia, David Dao, Boxin Wang, Frances Ann Hubis, Nezihe Merve Gurel, Bo Li, Ce Zhang, Costas J. Spanos, Dawn Song. Efficient Task-Specific Data Valuation for Nearest Neighbor Algorithms. VLDB 2019.
Ruoxi Jia, David Dao, Boxin Wang, Frances Ann Hubis, Nezihe Merve Gurel, Bo Li, Ce Zhang, Costas J. Spanos, Dawn Song. Efficient Task-Specific Data Valuation for Nearest Neighbor Algorithms. VLDB 2019.
Data provenance has been studied intensively by the data management community for
decades, but how can we reason about data influence for ML training? In previous
work we proposed to use Shapley value as one way to measure data influence.
However, Shapley value is often computationally infeasible to compute. In this
paper, we show that computing Shapley value can be computed in PTIME for models
with strong locality, and we can use these simpler models as a proxy for more
complex models!
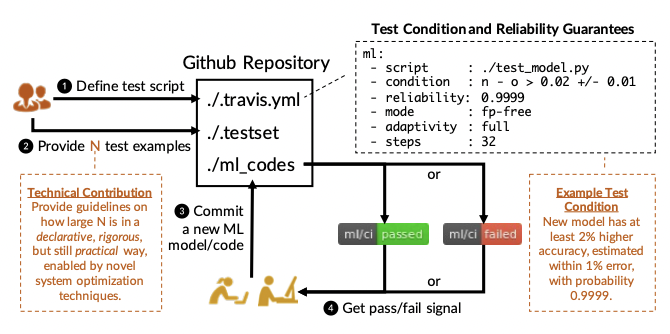 Cedric Renggli, Bojan Karlas, Bolin Ding, Feng Liu, Kevin Schawinski, Wentao Wu, Ce Zhang. Continuous Integration of Machine Learning Models: A Rigorous Yet Practical Treatment. SysML 2019.
Cedric Renggli, Bojan Karlas, Bolin Ding, Feng Liu, Kevin Schawinski, Wentao Wu, Ce Zhang. Continuous Integration of Machine Learning Models: A Rigorous Yet Practical Treatment. SysML 2019.
Continuous integration is an important functionality for modern software
development, how does a CI/CD framework for ML look like? In this paper, we
look at this problem and realize a unique challenge --- CI/CD for ML needs
to carefully manage test case reuse and overfitting. To this end, we provide
a statistically rigorous CI/CD framework rooted in adaptive analytics and
description length. To our best knowledge, this is one of the first early
prototypes of CI/CD for ML.
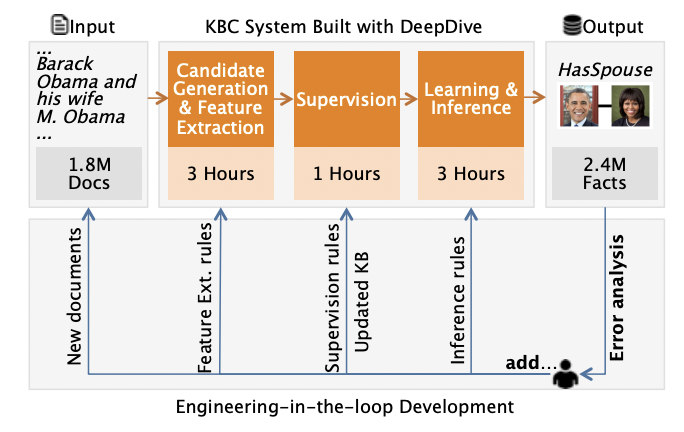 Jaeho Shin, Sen Wu, Feiran Wang, Christopher De Sa, Ce Zhang, and Christopher Re. Incremental knowledge base construction using DeepDive. VLDB 2015. (SIGMOD Research Highlight Award)
Jaeho Shin, Sen Wu, Feiran Wang, Christopher De Sa, Ce Zhang, and Christopher Re. Incremental knowledge base construction using DeepDive. VLDB 2015. (SIGMOD Research Highlight Award)
Knowledge-base construction is a task that is inherently knowledge-rich. DeepDive
is a framework that we developed for years to provide declarative knowledge
integration and statistical reasoning at scale. It has enabled a diverse range
of applications, from Paleontology, to anti-human trafficking.
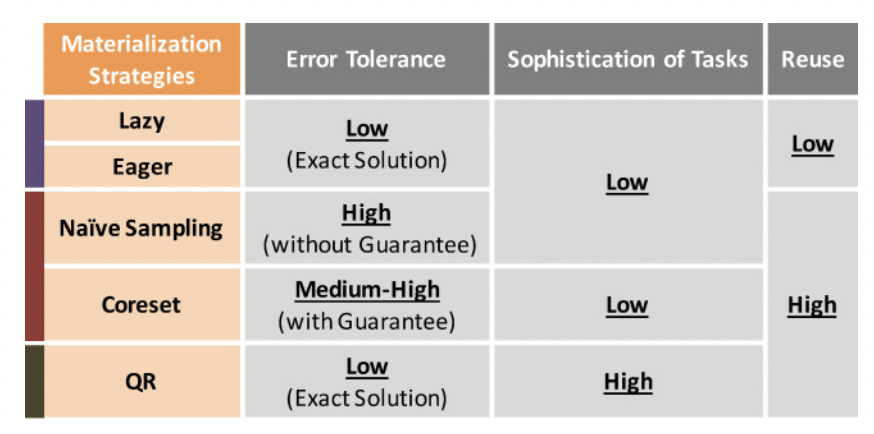 Ce Zhang, Arun Kumar, and Christopher Re. Materialization optimizations for feature selection workloads. SIGMOD 2014. (SIGMOD Best Paper Award)
Ce Zhang, Arun Kumar, and Christopher Re. Materialization optimizations for feature selection workloads. SIGMOD 2014. (SIGMOD Best Paper Award)
A declarative framework for feature selection, which automatically optimizes
and manages the tradeoff. It is amazing to see how traditional data management
concepts (such as materialization) can be applied to ML, and see the unique
challenges and opportunities that ML imposes to these traditional concepts
given different levels of error tolerance.